Part Two: Treatment of Trigeminal Neuralgia
III. Surgery
A. Overview
Neurosurgical interventions are considered when medical therapy proves ineffective in controlling TN pain. Each type of surgery carries with it potential benefits as well as risks of complications or long-term side effects. Thus, one must select the type of surgery carefully, with a complete understanding of all possible outcomes. None of the surgical interventions are effective in every case, and there is no way to accurately predict who will benefit from which procedure. The results of any procedure are known to be dependent upon the experience, expertise, and specific techniques unique to the neurosurgery team. These important variables must be taken into account when selecting a treatment.
The various treatment options are summarized and illustrated in the following chart:
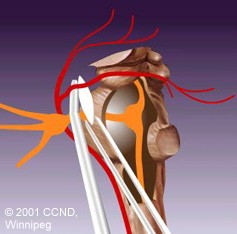
| Microvascular Decompression Surgery alleviates neurovascular compression by placing inert shredded Teflon?? felt implants between offending vessels and the trigeminal nerve root. | |
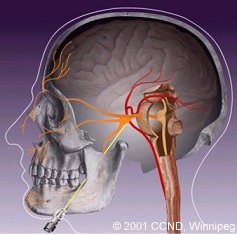
| Percutaneous Rhizotomies involve inserting a needle through the cheek and into an opening at skull base (foramen ovale). There, a controlled injury to the trigeminal nerve and Gasserion ganglion may be produced in one of three ways: | |
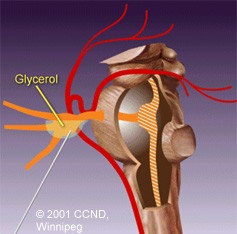
| 1) Percutaneous Glycerol Injection - glycerol is injected into the space around the Gasserion ganglion, and chemically damages the nervous tissue. | |
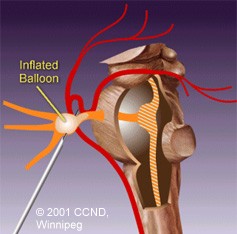
| 2) Percutaneous Balloon Compression Rhizotomy - a balloon is inflated next to the Gasserion ganglion, compressing and mechanically damaging the nervous tissue. | |
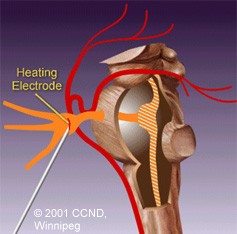
| 3) Radiofrequency Rhizotomy - an electrode is advanced into the Gasserion ganglion, and heated to thermally damage the nervous tissue. | |
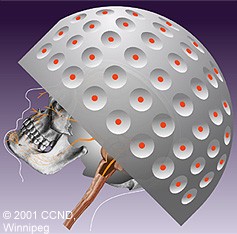
| Gamma Knife Radiosurgery focuses cobalt radiation upon the trigeminal nerve root, producing a delayed injury to nervous tissue that is similar to that produced by other percutaneous rhizotomy techniques. | |
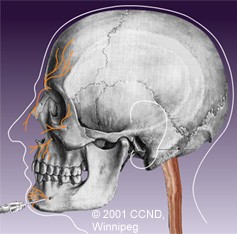
| Peripheral Trigeminal Nerve Blocks, Sectioning and Avulsions involve injuring the peripheral portions of the trigeminal nerve external to the skull. | |
| Microsurgical Rhizotomy involves surgical exposure and cutting of the trigeminal nerve root near its entry into the brain stem. | 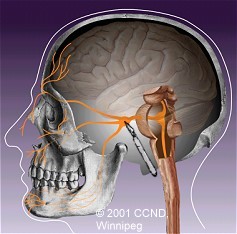 |
'Life > e—md—medicine' 카테고리의 다른 글
| JPT 5기 건강법으로 삶을 리모델링하다 (0) | 2007.09.14 |
|---|---|
| RN running to save lives!!! (0) | 2007.03.25 |
| 삼차신경통(Trigeminal Neuralgia) (0) | 2006.08.28 |
| Exploring the Link Between Conduct Disorder in Adolescence and Personality Disorders in Adulthood (0) | 2006.08.19 |
| Borderline personality disorder (BPD) (0) | 2006.08.19 |